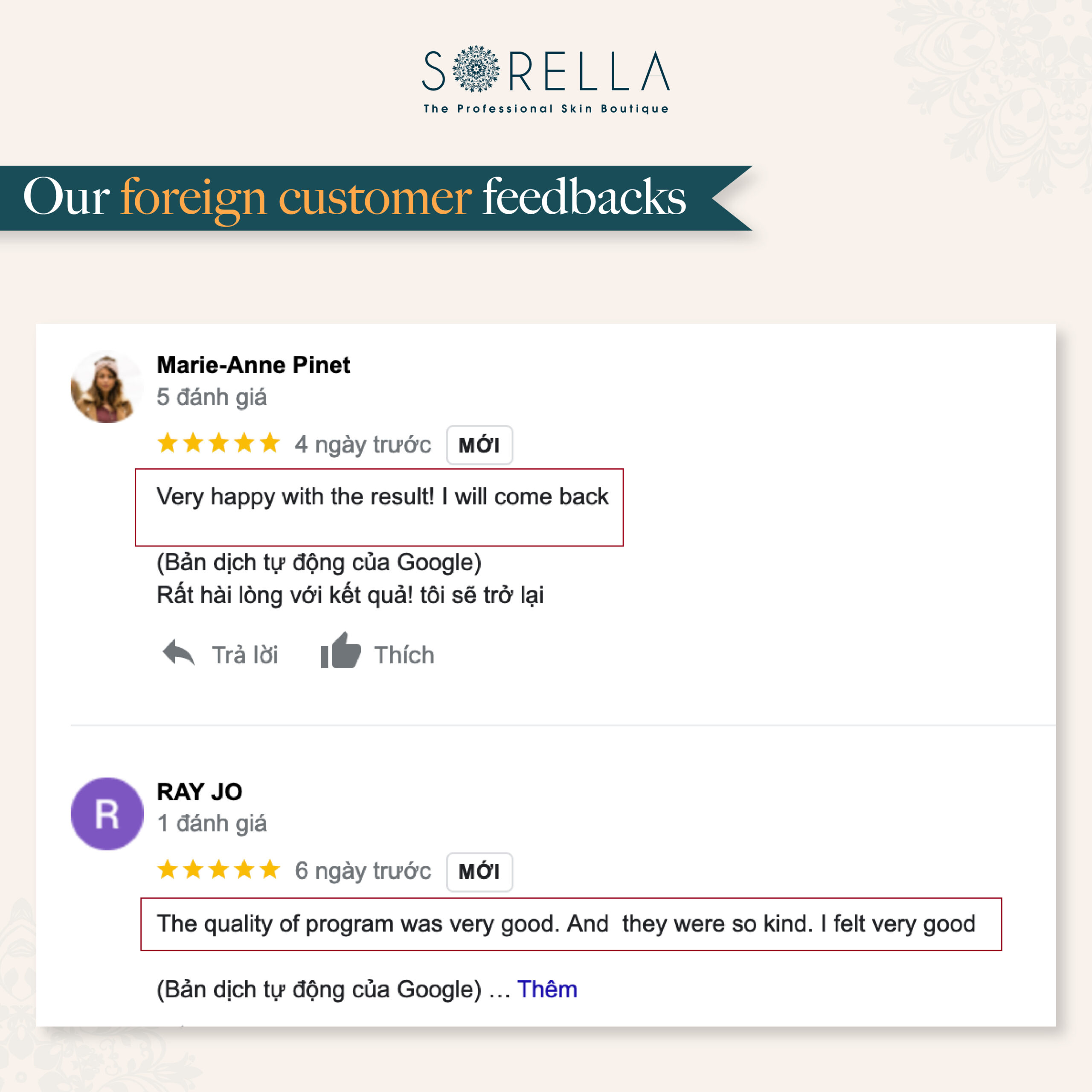
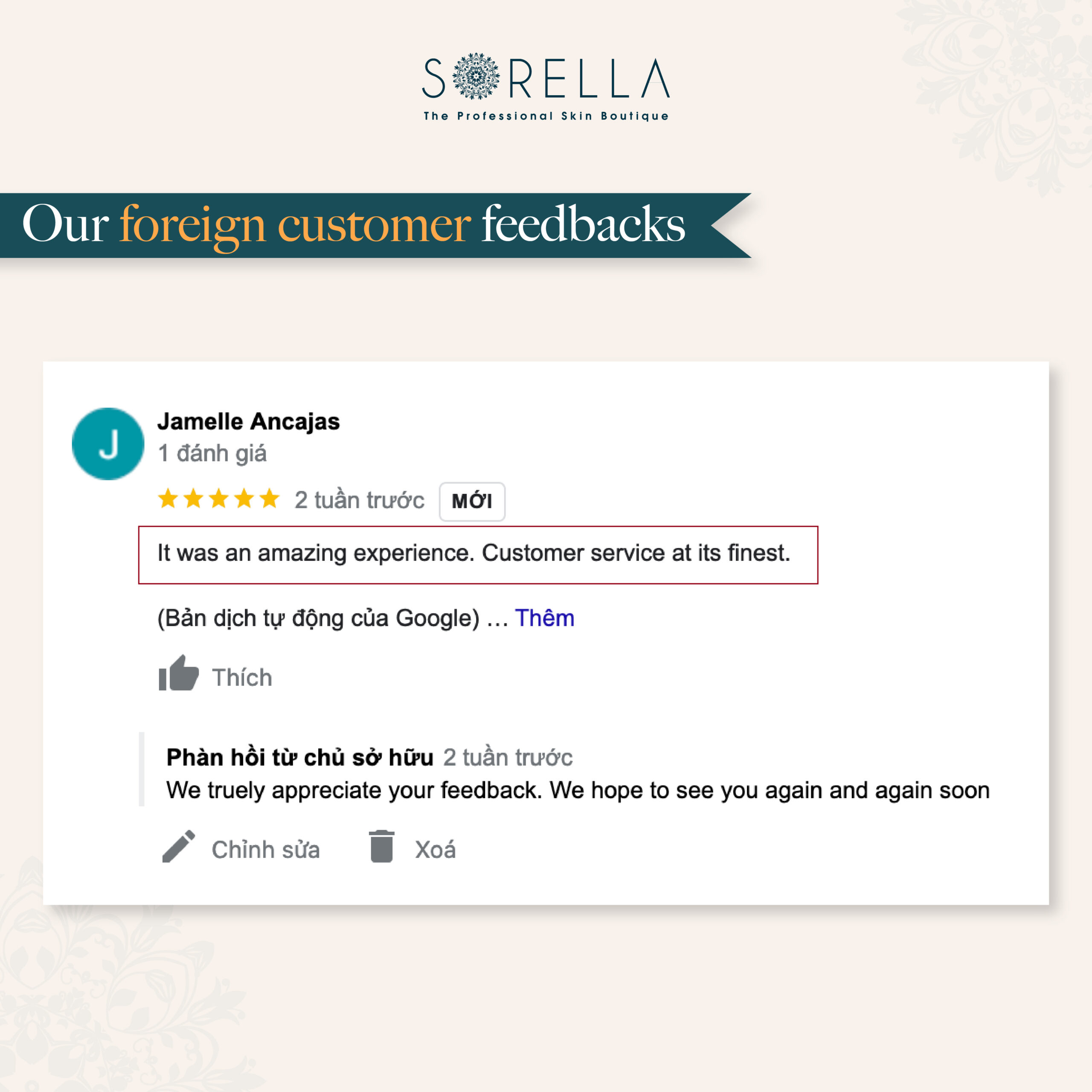
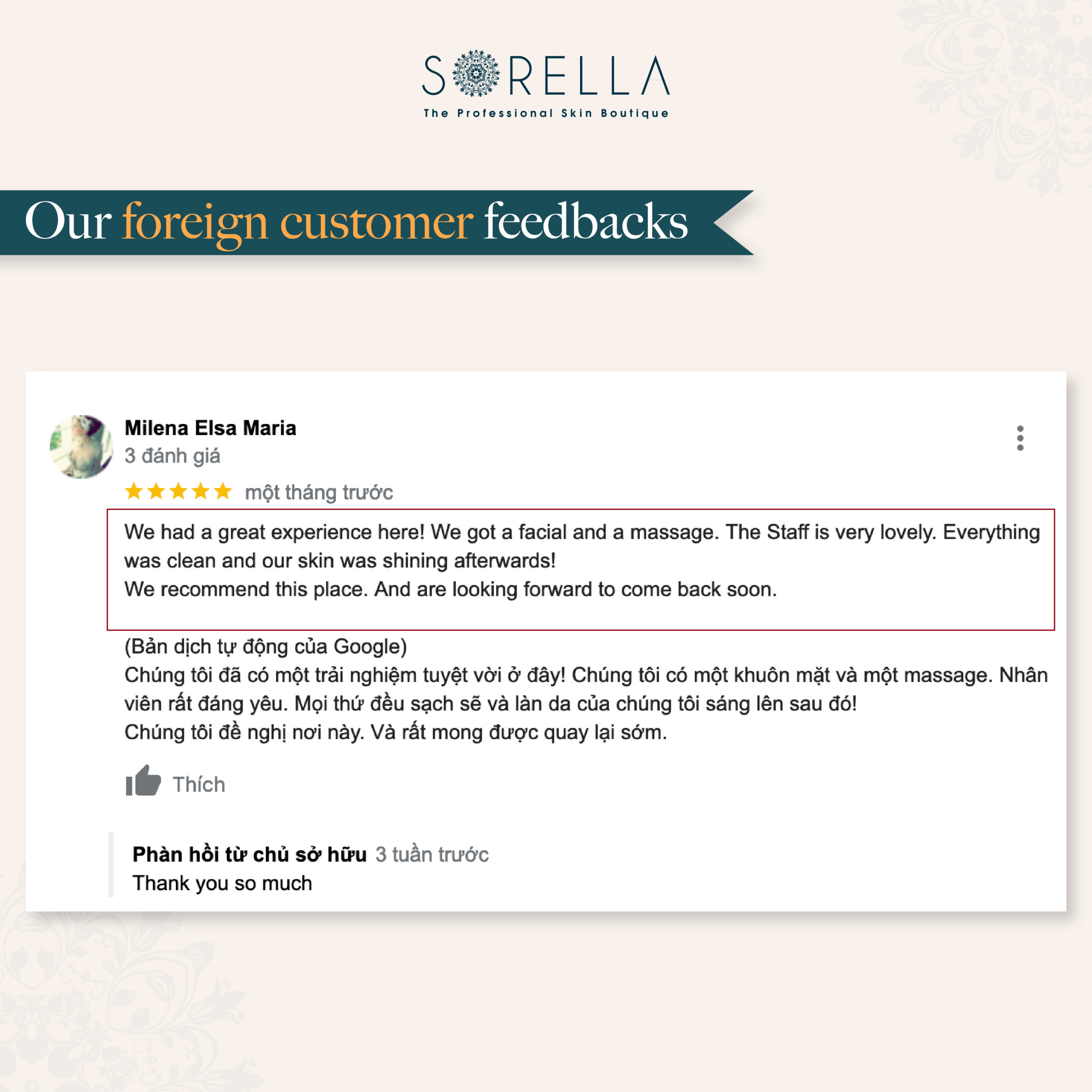
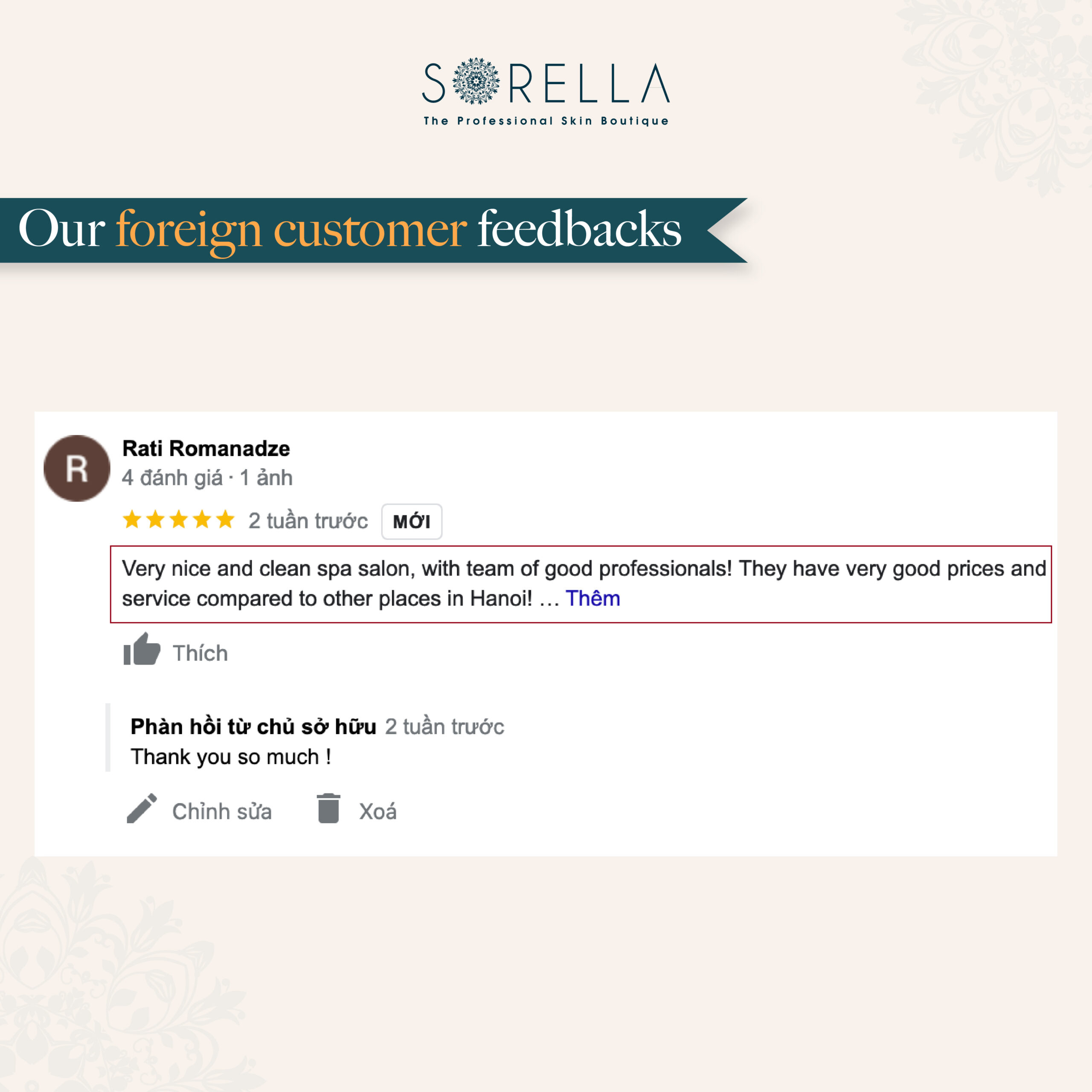
Bí quyết làm đẹp
Common Types of Skin Fungal Infections and 3+ Treatment Methods
Skin fungal infections are common, with a prevalence rate of around 27%. These infections can be transmitted from person to person, especially within families, if sharing personal items, sleeping together, or not paying attention to personal hygiene.
1. Causes of the Prevalence of Skin Fungal Infections
The climate in Vietnam is the first factor to mention. Located in a humid tropical area, this condition is very conducive to the spread and development of various types of skin fungi.
Fungi are low organisms that lack the ability to synthesize organic matter on their own, unlike other types of plants. Therefore, to survive, they must parasitize hosts. Hosts can be any source of infection around us, such as the environment (air, plants, soil,…), animals (dogs, cats,…) and even humans. As a result, the infection rate of this disease is very high and it has become a common illness.
Additionally, an unscientific lifestyle also creates favorable conditions for the development of skin fungi. Specifically:
- Fungi thrive in environments with high alkalinity and pH ranging from 7 to 7.2.
- Poor hygiene leading to fungal infections in closed areas and places that easily sweat such as the fingers and toes. Improper use of soap also increases the risk of infection.
- Humid environments, excessive sweating, and wearing tight clothing in temperatures ranging from 27 to 35 degrees Celsius also promote fungal growth.
- Excessive use of antibiotics, immunosuppressants, or hormonal imbalances in women can also be causes of fungal infections.
>> See more: What is Hifu? 5+ benefits of Hifu for women
2. Common Types of Skin Fungal Infections
2.1. Ringworm
Fungi from the Dermatophytes group play a crucial role in causing ringworm, a quite common skin condition. Initially, patients may only experience mild itching, but it later develops into red rings with small blisters around. If not treated promptly, the infection tends to spread into different rings.
Ringworm can spread quickly through scratching by the affected person. This is because the disease can be transmitted from person to person through sharing personal items such as towels, beds, or clothes.
2.2. Pityriasis Versicolor
Pityriasis versicolor is a common skin condition, especially in tropical regions, with 30-40% of the population affected at some point. The warm and humid climate is favorable for the growth of the causative fungi.
The disease usually occurs in adolescents and young adults. Some factors that can facilitate the disease include oily skin, excessive sweating, weakened immune system, poor nutrition, pregnancy, and corticosteroid use.
The cause of pityriasis versicolor is fungi from the Malassezia group. Lesions caused by pityriasis versicolor are round or oval with fine scales. To detect these scales, one can gently scrape the surface of the lesion. These lesions can merge to form large patches with multiple rings. Common locations of lesions include areas that sweat, especially the chest and shoulders.
Lesions can also appear on the face (common in children), scalp, elbows, under the breasts, and around the anus. Common colors of lesions include brown (due to hyperpigmentation) and yellow-brown (due to hypopigmentation); sometimes mild inflammation causes a pink color.
Patients may experience mild itching, especially on hot days.
2.3. Athlete’s Foot
Fungi such as Epidermophyton and Candida albicans are considered causes of athlete’s foot, also known as intertrigo or trench foot. Those who frequently immerse their feet in water for prolonged periods are more susceptible to this disease, such as farmers working in rice fields, sanitation workers without proper protective equipment, and swimmers.
Athlete’s foot usually presents in three different forms: vesicles containing fluid, intertrigo, and dry scaling. To treat this disease, it is necessary to follow the preventive and treatment guidelines from healthcare professionals.
2.4. Nail Fungus
Nail fungus, also known as dermatophytes, accounts for more than 90% of nail fungal infection cases. It often appears at the free edge of the nail or along the sides and can spread from nail to nail. Nail fungus causes the nail to lose its color, become brittle or elevated, and the surface of the nail may develop pits or deep grooves with powdery debris underneath. The patient’s nails become increasingly rough, turning from white to yellow or whitish-yellow.
Candida albicans can also cause nail fungus. This type of fungus affects the inside of the nail, causing damage and irregular growth with rough patches. The surrounding skin may also become red and swollen, and in severe cases, pus may appear.
2.5. Scalp Ringworm
This condition is caused by fungi that infect the scalp, leading to symptoms such as itching, swelling, red patches, and even hair loss. Scalp ringworm often affects children but can also occur in adults. Treatment typically involves topical or oral antifungal medications, so diagnosis and treatment usually require the intervention of a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist or pediatrician.
3. Are Skin Fungal Infections Contagious?
Are Skin Fungal Infections contagious? Skin fungal infections are highly contagious and can easily spread to other parts of the body and to other individuals. These infections can be transmitted through direct contact with fungal spores present in the environment, on skin, clothing, or towels. Environmental spores are ubiquitous, found in soil, air, water, and on various surfaces. Skin-to-skin contact, such as during physical activities or casual interactions, is a common way for these infections to spread.
Indirect contact through contaminated objects like clothing, towels, and personal items also plays a significant role. Sharing beds, bedding, hairbrushes, or footwear can facilitate the transfer of fungal spores. Pets, including cats, dogs, and small rodents, can be carriers and transmit the infection to humans through direct contact or by contaminating household surfaces.
Livestock and other animals can also be sources of fungal infections, especially for those who work closely with them. Several factors contribute to the contagion of fungal infections. Poor personal hygiene, such as not washing hands regularly or failing to bathe properly, increases the risk. Public places like gyms, swimming pools, and locker rooms are hotspots due to their warm and moist environments, which are ideal for fungal growth. Walking barefoot in these places heightens the risk of contracting an infection.
Cuts, abrasions, and other skin injuries provide an entry point for fungal spores, so keeping wounds clean and covered is crucial. Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or those undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible. Humid and warm climates, like that of Vietnam, further promote fungal growth and spread, making infections more common during hot and humid seasons.
Wearing tight and non-breathable clothing can create a moist environment that encourages fungal growth. To prevent infections, it is essential to maintain good personal hygiene, avoid sharing personal items, wear protective footwear in public places, and regularly clean living spaces. Proper pet care and prompt treatment of skin injuries also help reduce the risk of fungal infections.
By understanding the contagious nature of skin fungal infections and implementing effective preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of contracting and spreading these infections.
>> See more: SHAVING – 5+ THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE SHAVING THAT EVERYONE SHOULD CONSIDER
4. Are Skin Fungal Infections dangerous?
Are skin fungal infections dangerous? Skin fungal infections are not typically dangerous if diagnosed and treated promptly. However, untreated or neglected infections can cause several issues, including:
- Swelling, itching, and discomfort: Fungal infections often cause itching, swelling, and red skin, leading to discomfort.
- Prolonged infection: Some cases of fungal infections can lead to prolonged skin infections that spread to other areas.
- Changes in appearance: Fungal infections of the nails or skin can alter the appearance and color of the affected areas.
- Hair loss: Scalp ringworm can cause hair loss in the infected areas.
- Contagion risk: Some types of fungal infections can spread from person to person.
- Psychological and physical discomfort: Prolonged symptoms can lead to significant discomfort and psychological impact.
5. Treatment of Skin Fungal Infections
For most common skin fungal infections, these conditions are usually not dangerous and do not cause serious health issues. However, they can easily spread and affect daily life by causing itching and discomfort.
When not treated promptly, the disease can persist for a long time, be difficult to eliminate entirely, and can recur multiple times, often more severely with each recurrence. This makes treatment more challenging.
Therefore, when you notice signs suggesting you might have a fungal skin infection, seek a dermatologist for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Many medical facilities, hospitals, and dermatology centers are available to help people find a place for fungal infection treatment. You should seek reputable locations for an accurate diagnosis of your condition.
The treatment of fungal skin infections should be tailored to each specific case. In such cases, doctors may prescribe topical medications to be applied directly to the affected skin areas to treat filamentous fungal infections. Medications such as Clotrimazole, Ciclopiroxolamine, Ketoconazole, etc., may be prescribed. Patients should follow the doctor’s instructions and attend follow-up visits to monitor their condition and adjust the treatment as needed.
To quickly improve the condition, patients need to change some lifestyle habits. First, maintain personal hygiene, wear clean, loose clothing, and choose breathable footwear. Avoid walking barefoot in public places like locker rooms or gyms. If suffering from athlete’s foot, avoid wearing shoes.
Additionally, washing clothes thoroughly with soap and drying them in strong sunlight helps kill bacteria. Washing underwear frequently is particularly important. Patients should avoid contact with infection sources from animals and never share personal items with someone who has a fungal infection.
During treatment, patients should avoid using products with many chemicals for cleaning, such as detergents and soaps. Instead, only bathe with clean water and choose mild products. If necessary, consult a doctor for suitable product recommendations.
Finally, regular cleaning to maintain a clean living environment is important. Hopefully, this article has provided useful information about common skin fungal infections today. Given the easy transmissibility of these infections, maintaining good hygiene is essential to reduce the risk of contracting the disease. When experiencing suspicious symptoms, you should visit a hospital for timely diagnosis and treatment to prevent the spread and prolong recovery time for unaffected skin areas.
>> See more: Top 9 spas with the best quality hair removal services addresses near me in Hanoi
6. Home treatment for Skin Fungal Infections
Self-treating skin fungal infections at home can be a temporary method to alleviate symptoms, but it is important to discuss with a doctor or healthcare professional before starting any self-treatment. This is especially crucial if symptoms become severe or persist.
Here are some methods to consider for self-treating skin fungal infections at home:
- Use antifungal creams: Over-the-counter antifungal creams can be purchased at pharmacies. Follow the usage instructions carefully and apply consistently for the recommended duration.
- Use over-the-counter antifungal medications: Medications like miconazole or clotrimazole can help control symptoms of fungal infection.
- Maintain skin hygiene: Keep the skin dry and clean. Use mild soap and warm water to wash daily, then thoroughly dry with a soft towel. Ensure the skin is not damp for prolonged periods.
- Change habits: If fungal infections frequently recur, consider changing habits and conditions that favor the skin. This may include changing the quality of shoes, and the type of socks, and limiting exposure to moist or oily conditions.
- Avoid public moist areas: Avoid places like gym locker rooms or swimming pools if you suspect a fungal infection.
7. Preventing skin fungal infections
Preventing skin fungal infections is crucial for maintaining healthy skin. Here are some ways to reduce the risk of fungal infections:
- Personal hygiene: Wash skin daily with soap and warm water, then thoroughly dry.
- Clean, dry clothing: Avoid wearing tight, non-breathable clothing. Choose natural fiber clothing that allows the skin to breathe.
- Avoid sharing personal items: Do not share towels, clothes, or other personal items with others.
- Wear protective footwear: Use footwear in public places like gyms, pools, and locker rooms.
- Maintain a clean living environment: Regularly clean the living area to prevent mold growth.
- Monitor pets: Ensure pets are checked for fungal infections and treated promptly.
By following these prevention measures, you can minimize the risk of developing skin fungal infections and maintain healthy skin.
Tư vấn chuyên môn bài viết:
TS.BÁC SĨ NGUYỄN HỮU QUANG
- Mô tả chi tiết dịch vụ DETOX TRỊ MỤN VIÊM LỖ CHÂN LÔNG tại SORELLA BEAUTY & SPA: 5+ Bước cần thiết
- Top 5 sản phẩm chứa Azelaic Acid trong chăm sóc da được bác sĩ da liễu khuyên dùng
- 10 bài tập giúp mắt hết dại đơn giản, dễ thực hiện
- Quy trình 4 bước cấy mi sinh học nano chuẩn y khoa
- Làm đẹp bằng vi kim tảo biển và 6 điều cần biết
Bài viết cùng chủ đề:
-
Nên lựa chọn Rejuran hay Karisma?
-
So sánh Karisma và Profhilo – 2 phương pháp trẻ hóa da tầng sâu đỉnh cao
-
Cách diệt chấy rận hiệu quả ngay tại nhà, 8 phương pháp tiêu diệt chấy rận hiệu quả
-
Có nên dùng khăn ướt để tẩy trang? Cẩn thận khi dùng khăn giấy ướt giúp chăm sóc làn da của bạn, 1 vài thành phần của giáy ướt có hại cho da


 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国) 한국어
한국어 English
English